Antivirus Self-Protection Test (September 2010)
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Types of Attacks was Analyzed for Self-Protection
Introduction
Online criminal activities are gaining momentum faster than ever. Both the rate at which new types and modifications of malicious programs appear and the complexity of malware are on the rise. Cybercriminals use increasingly sophisticated methods, including masking the presence of a malicious program in the system, compression, encryption and incapacitating antivirus solutions.
Social engineering techniques make it easy to entice users to download and launch malicious programs as yet unknown by antivirus solutions. In such cases, in order to gain complete and uninterrupted control over the system, malicious programs search for an antivirus program, firewall or other protective solution in order to disrupt its operation.
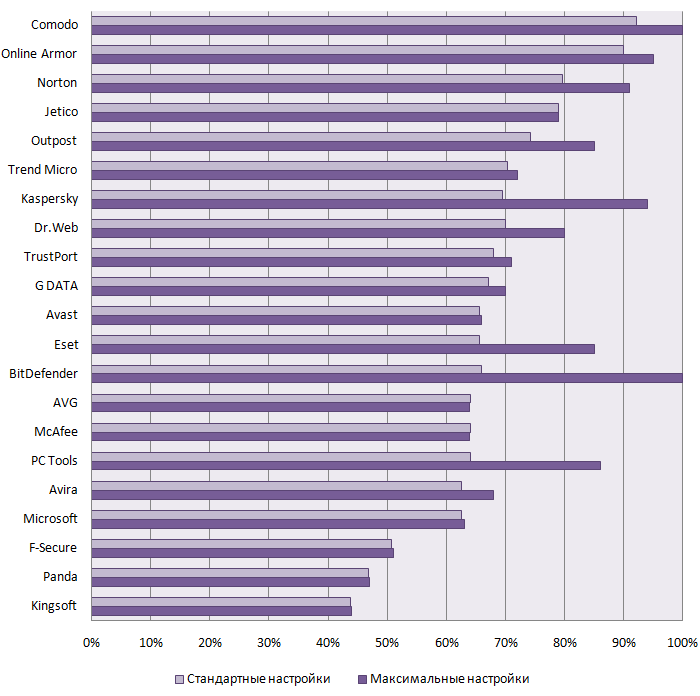
Consequently, contemporary antivirus products should be able to resist such attempts, that is, they should include self-protection functionality. This helps them to resist even the most complicated attacks, such as when malicious programs use a variety of methods to disable protection, and remove the infection using standard tools after receiving the appropriate antivirus database updates.
In the test described below, we analyzed the self-protection capabilities of antivirus solutions that run under Windows XP SP3 and Windows 7 x86.
Types of Attacks was Analyzed for Self-Protection:
- Modification of file and registry key access permissions.
- Modification / removal of modules.
- Deletion of antivirus databases.
- Modification / deletion of important registry keys.
- Process termination.
- Modification of processes / code.
- Driver unloading.
Methodology for Self-Protection Test »
Awards Guide of Self-Protection Test »
- Login to post comments